What is Civil Disobedience? Should it be Criminalized?
Civil disobedience has made a dramatic return to the American cultural landscape (not that it ever really left). Media reports featuring images of balaclava-wearing Antifa activists, Black Lives Matter protesters, silent football players, and armed militia members occupying federal buildings are the stock and trade of cable news and social media streams. Not surprisingly, the act of protesting remains controversial even as it is understood to be a form of or “free speech” – but this is complicated as we will see.
Technically guaranteed by the first amendment of the U.S. Constitution, nonetheless, we find that almost daily protesters are being arrested, pepper-sprayed, and beat up. Why is this happening? Why do we seem to care less about the 1st Amendment establishment than we do the 2nd Amendment’s “right of the people to keep and bear arms.” Presently, the two appear to be on a collision course as U.S. public debate steers into an increasingly violent territory.
Civil disobedience often involves the refusal to obey laws coupled with demands aimed at achieving political goals by influencing legislation and government policy. The refusal to obey is generally enacted on the basis of a belief the law is morally wrong. In some cases, civil disobedience can be passive, even silent. Yet the goal remains the same – to provoke a public spectacle and call attention to issues that activists deem important and worthy of protest.
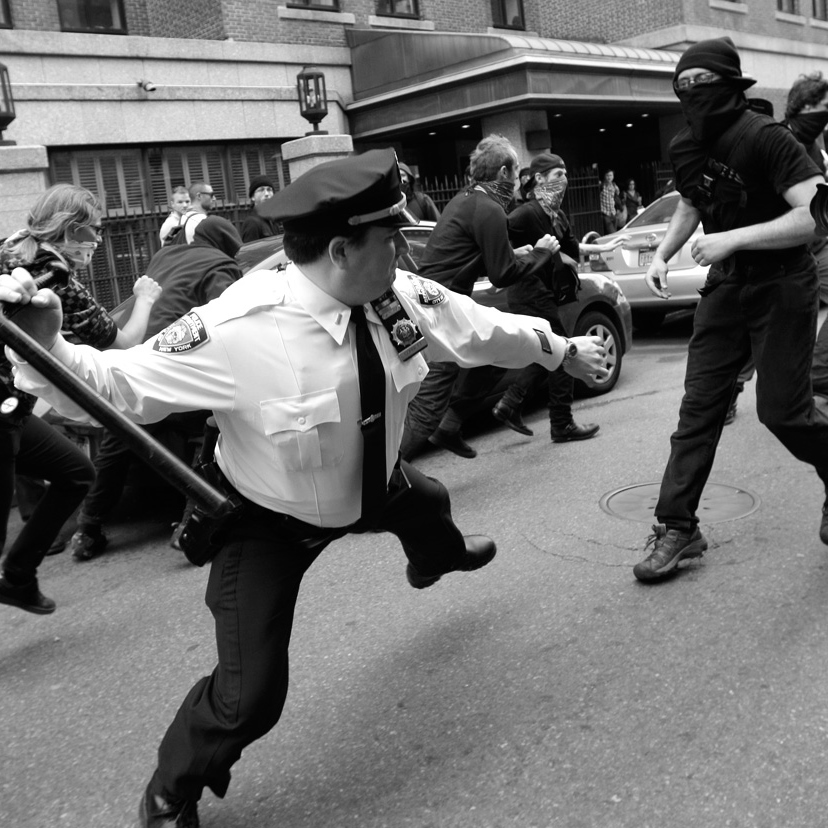
A New York City Police Supervisor winds up on an Occupy Wallstreet protester.
Civil disobedience is also sometimes referred to as non-violent/passive resistance. This was famously practices by some members of the U.S. civil rights movement, most notably by the followers of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., who employed it as part of a collective effort to protest social injustice (i.e. the segregation of public facilities). Non-violent techniques of protest include boycotting, sit-ins, picketing, marching, and the nonpayment of taxes. More violent efforts, however, may involve more disruptive actions, including violent physical confrontation.
Recently, debates on civil disobedience and protests have taken a turn into territory that would have previously been dismissed as hyperbolic and out of fashion. Nazi comparisons have risen to the fore and so scholars find they must address the contemporary packaging of old ideas thought to have been discredited, which have been given new life to a new audience in popular discourse.
Wanna Protest? Get a Permit…or Not?
There is a fine line to negotiate between free speech and disorderly conduct. Many protestors have argued that they were arrested for simply passing through an area or for standing on a public sidewalk. This crosses the line into police intimidation of free speech and remains a problem in many cities and towns that have been sites of public protest. So what is the guidance here? What is to be considered “reasonable” protest?
The First Amendment guarantees the right to assemble and the right to free speech and expression; however, there are limits on those rights. According to the American Civil Liberties Union, the government can in some cases require a permit as a condition of protest on public property; they can and do restrict the time, place, and manner of protest. This is why there are enforceable noise and time restrictions imposed in residential areas.
Additionally, just because people are protesting, they are not given free rein to break already existing laws. Simply walking on the highway or any roadway outside of a crosswalk is considered jaywalking, which is a crime. Furthermore, most jurisdictions also have laws regarding blocking or obstructing traffic.
Experts like Geoffrey Stone, a professor specializing in constitutional law at the University of Chicago, note that “Things like noise, blockage of ordinary uses of the place, blockage of traffic and destruction of property allow the government to regulate speakers.” The government, as the ACLU explains, often requires a permit for parades in the streets, given the impact on vehicle traffic. Likewise, the government often can require a permit for large protests in public parks and plazas, as part of an effort to ensure fairness that all groups might access the site (ACLU website).
Alternatively, a large majority of Occupy Wall Street-related arrests were based on charges alleging disorderly conduct, even as protesters argued that they were peaceably protesting. The arrests were justified on the basis of the New York Penal Code, which stipulates that anyone who makes “unreasonable noise,” obstructs “vehicular or pedestrian traffic,” or congregates “with other persons in a public place and refus[ing] to comply with a lawful order of the police to disperse” is a reasonable target for arrest.
Put another way, the First Amendment generally bars the government from requiring a permit when one person or a small group protest in a park, or when a group of any size protest on a public sidewalk in a manner that does not burden pedestrian or vehicle traffic. Such non-permitted protests might involve speeches, press conferences, signs, marches, chants, leaflets, expressive clothing, and efforts to speak with passersby. The absence of a permit for such protests simply does not burden any legitimate government interests. Thus, the Chicago Park District does not require a permit for gatherings in parks of fewer than 50 people. Likewise, the Chicago ordinance regulating public assembly does not require a permit for gatherings and marches on sidewalks that do not obstruct the normal flow of pedestrian traffic (ACLU website).
Briefly put, the First Amendment limits the kinds of permit fees and other financial burdens that government can impose on protesters. Blocking traffic may not be legal – it’s certainly nothing new for protesters – though it is time-honored and calculated form of civil disobedience. Protests are, by design, supposed to be inconvenient and provocative; they aim to awaken us from the soporific rhythms of daily life in order to call attention to a cause/problem citizens deem worth protesting.
So there is a question that remains with regard to how much inconvenience the authorities are willing to tolerate to accommodate First Amendment activity. This creates a gray area with regard to enforcement activity. The question remains – What is reasonable?
Contemporary Debates – Power, Politics, & Protest
Human rights historian, Dartmouth College Lecturer, and former Occupy Wall Street organizer Mark Bray recently came under fire when Dartmouth President Philip J. Hanlon repudiated Bray in a statement saying that he was “supporting violent protest.” His letter stated: “As an institution, we condemn anything but civil discourse in the exchange of ideas.” “The endorsement of violence in any form is contrary to Dartmouth values.”
Bray’s critique came to the attention of the Dartmouth administration when he was featured in media reports in the wake of the deadly “Unite the Right” rally in Charlottesville, Virgina. An expert on anti-fascism and antifa, Bray’s book, The Anti-Fascist Handbook, provides perspective on the movement. The book includes a survey of the history of antifa, where he explores its origins to the present day. Based on interviews with anti-fascists from around the world, Bray details the tactics of the movement, the philosophy that motivates it, and offers much-need insight into the contemporary moment of resistance.
Both Bray and George Ciccariello-Maher have written extensive critical commentary about Antifa; they are recommended reading for anyone that wants to acquire a deeper understanding of antifa and how they operate.
Unite the Right Ralley, Charlottesville, Virginia, 2017
In a “Meet the Press” interview, Bray framed the counter-protesters as defensively confronting the white supremacists who organized the rally, hinting that the violence was under some circumstances warranted, even justified. In light of this, the university sought to distance itself from him in the form of a letter published by its President.Dartmouth’s faculty, by way of contrast, stood behind Bray’s position; more than 100 faculty members at Dartmouth signed a letter calling on the president to retract the statement. They argued in support of Bray, who they said did not advocate for violence; rather, he noted that historically normal channels, including public debate and electoral politics, were not successful in thwarting the growth of fascism. Nothing in these remarks, they pointed out, violated Dartmouth’s free speech and academic freedom policies, they said. “Instead, in this case, Professor Bray has been disavowed by Dartmouth at the request of a right-wing organization, Campus Reform” (Hawkins)
Dartmouth’s faculty, however, took a decidedly different view and stood behind Bray’s position. The problem, according to the faculty, was Hanlon’s statement, which they argued reduced the term ‘violent protest’ to such an extent it lumped together all acts of radical politics, acts of civil disobedience, and resistance to authority, and thereby effectively conflated them with other acts of violent political “terrorism.” Hanlon’s usage of the term, in other words, set up a false equivalency between passive acts of civil disobedience (blocking roads, silent protests, lunch counter sit-ins) and willful acts of violence.
More than 100 faculty members at Dartmouth signed a letter and called upon the President to retract his statement. They further argued that Bray did not advocate for violence; rather, he merely called attention to the fact that normal channels, including public debate and electoral politics, were not historically successful in thwarting the growth of fascism. Nothing in these remarks, they pointed out, violated Dartmouth’s free speech and academic freedom policies. Instead, they maintained that Professor Bray was disavowed by the Dartmouth administration at the request of a right-wing organization, Campus Reform” (Hawkins)
What Bray did, in fact, say was that “when pushed, self-defense is a legitimate response to white supremacist and neo-Nazi violence.” He went on to say that “We’ve tried ignoring neo-Nazis in the past. We’ve seen how that turned out in the ’20s and ’30s.” “A lot of people,” he said, “are under attack, and sometimes they need to be able to defend themselves. It’s a privileged position to say you never have to defend yourself from these kinds of monsters.” (“Meet the Press” interview).
The commentary, as well as the incident that provoked it (Unite the Right rally), made clear the fact that there are a wide variety of players on the field with respect to clashes between protesters and counter-protesters. Not all of them are the same and it is important that we clarify them, lest they are reduced to simple caricatures.
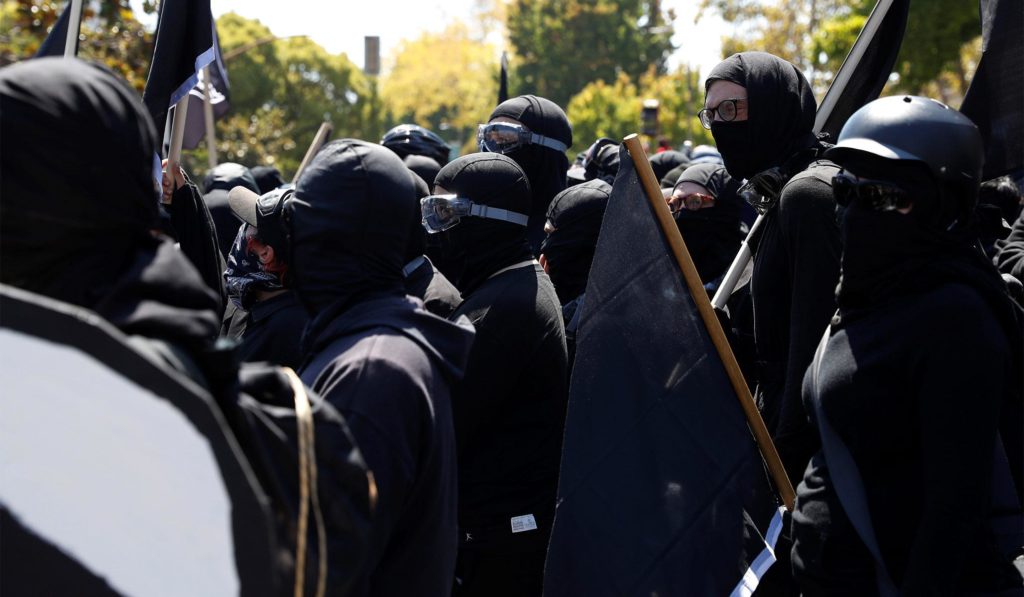
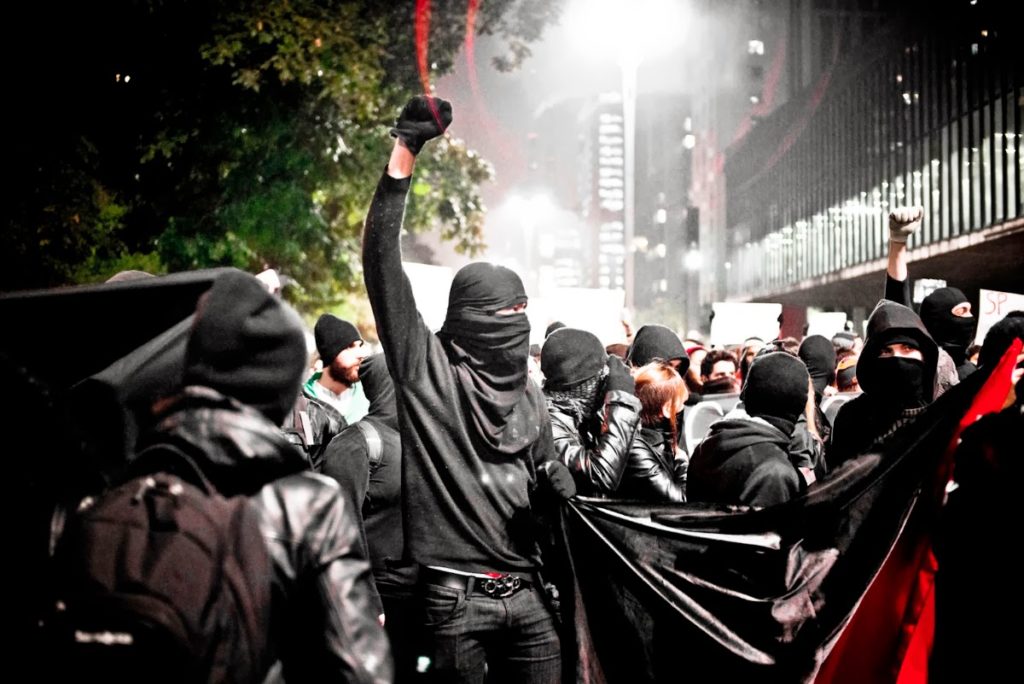
Antifa protesters in Berkeley, California
Who is Antifa? Who is Black-Bloc? Who is a Nazi?
The confusing array of actors that animate contemporary public debates about civil disobedience and free speech make it difficult for the average person to get a sense of what is happening. With that, acquiring a better-developed sense of the history of the rise of 20th-century fascism (s) is a social imperative. Reducing debate to competing dualisms and false equivalencies (i.e. “both sides” are responsible for the violence) – a favorite media tactic – tends to elide details that are important to distinguish.
Antifa
As long as there has been fascism, there has been anti-fascism — also known as “Antifa.” Antifa is a loose network of activist groups (the name is a contraction of the words “anti” and “fascist”). With roots in the European 1920’s/30’s resistance to Mussolini and Hitler, they are a far-left movement, whose members advocate using any means necessary, including violence, to combat capitalism, fascism, and white supremacy. Confrontation – physical if necessary – is a hallmark of its activism.
Recent political protests and acts of civil disobedience, many of which have been focused on resistance to the Alt-right movement and Trump administration policies, have featured black-clad activists wearing balaclavas covering their faces. Likewise, they have been pivotal players California college campuses, where they protested right-wing speakers.
Berkeley, Ca 2017
According to Bray, Antifa advocates for what is “basically a politics or an activity of social revolutionary self-defense. It’s a pan-left radical politics uniting communists, socialists, anarchists and various different radical leftists together for the shared purpose of combating the far right.”
What are the goals of antifa? For one, they aim to deny fascists the opportunity to promote oppressive politics — by any means necessary. Consequently, they have become known for their willingness to use violence, which they say is morally defensible and necessary to defensively combat those who use violence to pursue their political goals. Critics, however, say that shutting down political adversaries is anti-democratic; antifa counters this with the argument that fascism does not negotiate or reason; that the horrors of fascism must never be allowed to triumph again.
Alt-Right activist and actual American Nazi, Richard Spenser, shown here before he was punched in the face at the Trump inauguration by a guy who likes to punch Nazis.
Antifa is also well-known for its “Punch a Nazi” proclamations. Should you punch a Nazi? According to Drexel professor George Ciccariello-Maher, the answer is: yes, you should! Ciccariello-Maher is the former Associate Professor of Politics and Global Studies at Drexel University (now a Visiting Scholar at Vassar) and the author of Decolonizing Dialectics; Building the Commune: Radical Democracy in Venezuela; and We Created Chávez: A People’s History of the Venezuelan Revolution. No stranger to controversy, he made national headlines for tweets about white genocide conspiracy theory. He has also written about the role of white supremacy in the killings of Trayvon Martin, Mike Brown, Freddie Gray, Philando Castile, in addition to the Ferguson and Baltimore protests.
Ciccariello-Maher has been criticized by right-wing websites for arguing in Salon that “Riots Work,” for arguing that reverse racism is imaginary, that the police should be abolished, and for tweeting “All I Want for Christmas is White Genocide.” He stated that his tweet was sent in response to the racist backlash against State Farm Insurance for advancing “white genocide” (State Farm depicted an interracial couple in one of its advertisements).
SKOKIE, IL – APRIL 19: Neo-Nazi protesters organized by the National Socialist Movement demonstrate near where the grand opening ceremonies were held for the Illinois Holocaust Museum & Education Center April 19, 2009, in Skokie, Illinois. About 20 protesters greeted those who left the event with white power salutes and chants. American Nazi (Photo by Scott Olson/Getty Images)
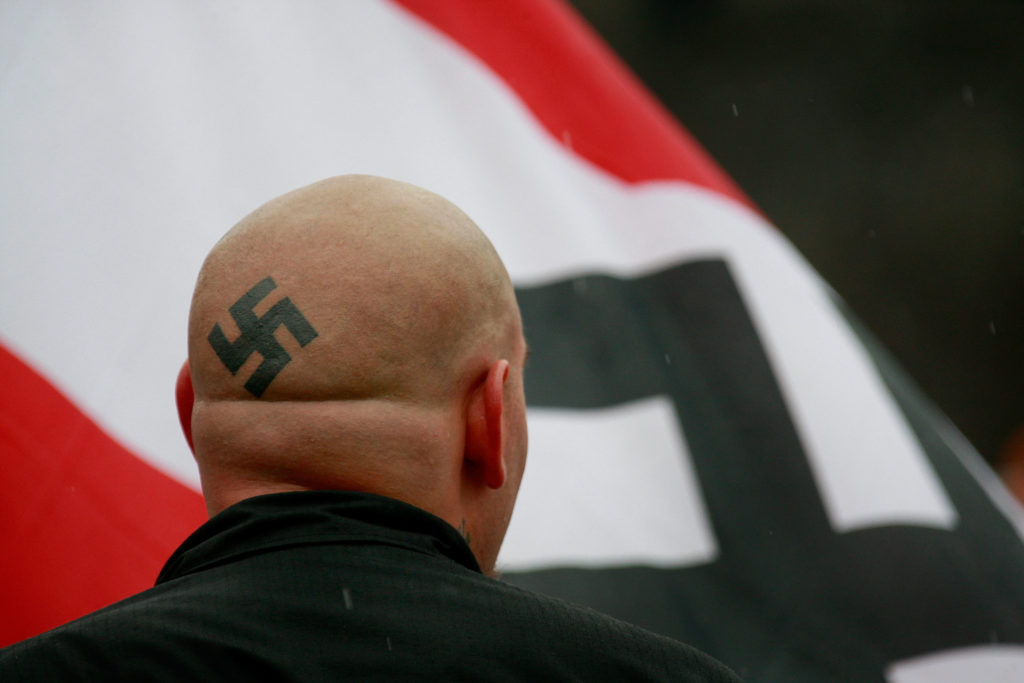
Nazis (American)
The most visible neo-Nazi group in the U.S. is the National Alliance. Until his death, it was led by William Pierce, the infamous author of the futuristic race-war novel The Turner Diaries, a book believed by some to have served as the blueprint for the 1995 Oklahoma City bombing.
According to the Southern Poverty Law Center, whereas some neo-Nazi groups emphasize simple hatred, others are more focused on the revolutionary creation of a fascist political state. Nazism, of course, has roots in Europe, and links between American and European neo-Nazis are strong and growing stronger. American neo-Nazi groups, protected by the First Amendment, often publish material and host Internet sites that are aimed at European audiences — materials that would be illegal under European anti-racism laws. Similarly, many European groups put up their Internet sites on American servers to avoid prosecution under the laws of their native countries (SPLC website).
Here it is worth noting that not all self-declared white supremacists identify as Nazis. Though this may be parsing the definition to the extent that it facilitates an effort to create social distancing among white supremacists, who prefer khakis and tiki torches to hoods and crosses. Bear in mind that to speak of the term Nazi” is to invoke a history characterized by images of death camps and genocide. The very term “Nazi” is almost anachronistic; it implies backward thinking and is suggestive of a less-enlightened time in our history.
The protest in Charlottesville was the first time the many Americans were treated to the chanting predilections of white nationalists, who are fond of shouting them at their rallies. They all hold particular meanings and enjoy wide circulation within the alt-right movement, particularly at online white-nationalist forums as well as chat sites like 4chan, but are unfamiliar to most of the general public (Niewert, 2017).
- “You Will Not Replace Us!” This slogan was coined from a statement by Nathan Damigo, founder of the white-nationalist campus group Identity Evropa, who retorted to an anti-Donald Trump “He will not divide us” campaign by actor Shia LeBeouf on social media: “Shia LeBeouf, you will not replace us with your globalism.” The chant is closely related to the white-nationalist “White Genocide” meme, reflective of their fears that white people and white culture are under attack from multiculturalism and nonwhite races. According to the Anti-Defamation League, the slogan began appearing on white-nationalist flyers and banners in May of 2017 and has spread widely since then (during the first Charlottesville march, the chant morphed into “Jews Will Not Replace Us!”)
- “Blood and Soil!” Possibly the most disturbing of all the chants heard in Charlottesville, this is the English rendition of Nazi Germany’s most fervent chant, “Blut und Boden!” Originally devised as a slogan of 19th-century German nationalists and popularized by Nazi ideologue Richard Walter Darre, the phrase is intended to invoke patriotic identification with native national identity, and built on a foundation of virulent anti-Semitism and racism. It later became a key component of Adolf Hitler’s “Lebensraum” program, seeking to expand territories occupied by Germans, that was a major factor in the Holocaust. The slogan has been adopted by the alt-right, particularly its openly neo-Nazi element, to emphasize its own nativist and eliminationist agenda.
- “White Lives Matter!” Ostensibly a retort to the anti-police-violence movement Black Lives Matter, this catchphrase very quickly morphed into both a slogan and the name of an outright white-supremacist movement aimed at attacking black civil rights, ostensibly “dedicated to the promotion of the white race and taking positive action as a united voice against issues facing our race.” Numerous neo-Nazi groups around the country have reshaped themselves under the “WLM” banner, and the movement was designated as a hate group in 2017.
- “Hail Trump!” This catchphrase needs little explanation, but its presence as a marching chant is significant. Donald Trump is a hero to the alt-right, where some leading figures refer to him as “Glorious Leader” and similar superlatives, in large part because he mimics their agenda and talking points, and has on numerous occasions shied away from denouncing white nationalists, including after Charlottesville. Many of the Charlottesville marchers have also worn Trump’s trademark “Make America Great Again” ball caps.
Alt-Right
The Alt-Right is a far-right racist movement that advocates an ideology based on white supremacy and anti-Semitism. The stated goal of the organization is the creation of a white ethnostate. Richard Spencer, one of the leaders of the movement, claims the “Alt-Right” is merely advocating a form of identity politics for white people.
Many of the men and women who descended upon the University of Virgina campus in Charlottesville, Virginia are advocates of Alt-Right identity even as they may be loath to identify as Nazis. The fact that many at the Saturday rally that carried flags with swastikas is, however, a matter of record.
The “Unite The Right” rally was organized by a white nationalist, Jason Kessler. Ostensibly, its purpose was to some extent fulfilled, as the aim was to unite the diversity of far-right groups, including everyone from Nazis to white nationalists, neo-confederate, identarian, and armed “Patriot” groups.

The groups depicted include from left to right (K) “Kekistani,” (AC) “Anti-Communist,” (L) “Libertarian,” (N) “Nationalist,” (I) “Identitarian/Identity Evropa,” (SN) “Southern Nationalist,” (NS) “National Socialist,” and (AR) “Alt Right.” The National Socialist flags depicted include Traditionalist Worker Party and Vanguard America.
In this instance, the choice of Charlottesville was not happenstance. The city itself stands as a monument to white supremacist patriarchy. There are the obvious symbols, the statuary commemorating Confederate Gens. Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson. Less obvious is the structural racism that emanates from the ideological underpinnings of America. Thomas Jefferson, a founding father of the country as well as the founder of UVA, famously objected to slavery even as he argued that African Americans could not be incorporated into the society at large on an equal basis with whites. That he did this while he himself owned slaves and fathered children with them is telling.
Black-Bloc
Black blocs are “ad hoc assemblages of individuals or affinity groups that last for the duration of a march or rally” in which members retain their anonymity via head-to-toe black clothing. Known for their use of force, the group also protests peacefully, where the primary objective is to “embody within a demonstration a radical critique of the economic and political system.” It should be noted the black bloc isn’t a group; rather, it is a tactic that permits radicals to engage in direct action without fear of arrest; while many black blockers are anarchist, not all of them are (Douglas-Bowers).
Black bloc originated in Germany, where they were affiliated with the autonomous movement in the 1980s. West German feminists were particularly influential to the extent that they provided the group with an anarchist spirit. The tactics used by the Automen included rent strikes, where buildings were turned into squats that became centers for political activity.
The first significant use of the black bloc tactic in the United States occurred at the Pentagon, in Washington, D.C. on 17 October 1988. Over one thousand demonstrators—a small number consisting of a black bloc—called for the end to U.S. support for the right-wing death squads in El Salvador. They appeared again at a January 1991 rally against the Persian Gulf War.
The Seattle protests in 1999, however, put them on the map in the U.S. The “Battle in Seattle” as it is known consisted of a series of protests that were launched in connection with the WTO Ministerial Conference of 1999, when members of the World Trade Organization (WTO) convened at the Washington State Convention and Trade Center in Seattle, Washington on November 30, 1999.
While the black bloc may be made up of militants, they are consistently categorized as hooligans, thugs, and youths who take joy in private property destruction (Douglas-Bowers).
Blac Bloc groups, not unlike the Antifas, have also worked to confront neo-Nazi and white supremacist groups.
In both the U.S. and Europe, Black blocs are typically white and male. However, there is some diversity. In a communiqué published days after the demonstrations against the 2001 G8 Summit in Genoa, Mary Black (a pseudonym for a protester who took part in the protests) noted that most of the people she knew who used black bloc tactics “have days jobs working for non-profits. Some are school teachers, labor organizers, or students. Some don’t have full-time jobs, but instead spend most of their time working for change in their communities. Consequently, if they did not have radical political and social agendas, they might be compared with nuns, monks, and others who live their lives in service (Douglas-Bowers).
Berkeley Protests, 2017
Not all black blockers engage in property destruction. While one may use black bloc tactics, there are different roles one can play. Groups take into account things such as a person’s immigration status, health problems, previous arrest record and the like, and at-risk individuals can engage in low-risk tasks such as being “in charge of legal support in the event of arrests, or responsible for transportation, lodging, water and food supplies, media contacts, psychological support” and whatnot (Douglas-Bowers).
With regards to property damage, for black blockers, the target is the message. Targets are often chosen for their symbolic value (Douglas-Bowers). The use of property destruction by some black blockers can cause problems, such as can be seen in the recent Berkeley protests, where people were protesting the death of Eric Garner and individuals came and broke the windows of a number of banks. This is deeply problematic as it took the attention off the death of Eric Garner and the larger issues surrounding police brutality against the black community, and put the attention on banks. Actions such as these can potentially create a space for the police to justify a crackdown on all protesters (Douglas-Bowers).
Rise Above Movement – RAM
RAM, a violent group based in Southern California, claims more than 50 members, who claim a devotion to athleticism as an aspirational ideal, through which they intend to regenerate Western manhood. Its’ group members organize weekend training activities that include boxing and other martial arts. With that, as the video investigation conducted by Propublica (a nonpartisan investigative journalism group) reveals, its members have been implicated in organized violence carried out at protests across the country, including Charlottesville, Huntington Beach, San Bernardino, and Berkeley.
For more on RAM, follow the link to the article and video.
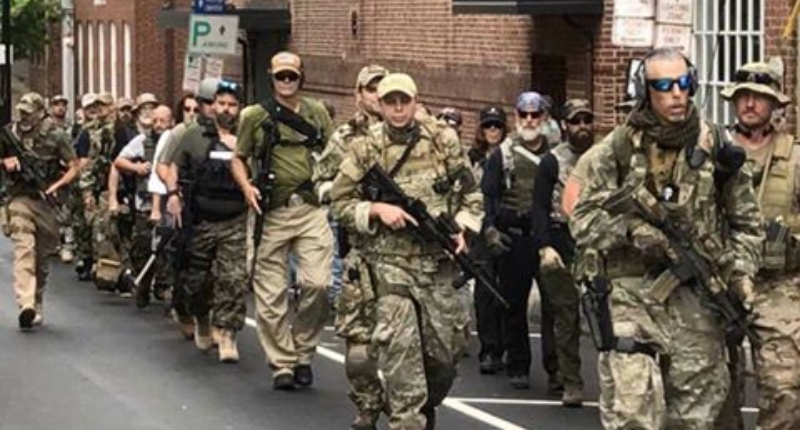
Militias & Anti-Government Groups
Militia organizations are motivated by a variety of ideologies and objectives. These include anti-tax, anti-immigration, survivalist, sovereign citizen, libertarian, land rights, and southern restoration ideologies. What they share in common is a belief in the potential rise of a tyrannical U.S. government, which they believe must be confronted by armed force if necessary.
The extreme right in the United States has long had a fascination with paramilitary groups. Before World War II, right-wing and fascist groups such as the Silver Shirt Legion and the Christian Front marched across America. Later, the Cold War ushered in a new wave of paramilitary organizations like the California Rangers and the Minutemen. In the 1980s, survivalists and white supremacists formed a variety of paramilitary groups ranging from the Christian Patriot-Defense League to the Texas Emergency Reserve to the White Patriot Party (ADL website).
The militia movement is heir to the right-wing paramilitary tradition, but it is heir, too, to another tradition, the anti-government ideology of groups like the Posse Comitatus. The Posse developed an elaborate conspiratorial view of American history and government, one that claimed the legitimate government had been subverted by conspirators and replaced with an illegitimate, tyrannical government. Posse members believed that the people had the power and responsibility to “take back” the government, through force of arms if necessary. As a result, many Posse figures engaged in paramilitary training. Most notable among these was William Potter Gale, a Christian Identity minister who was one of the founders of the Posse (ADL website).
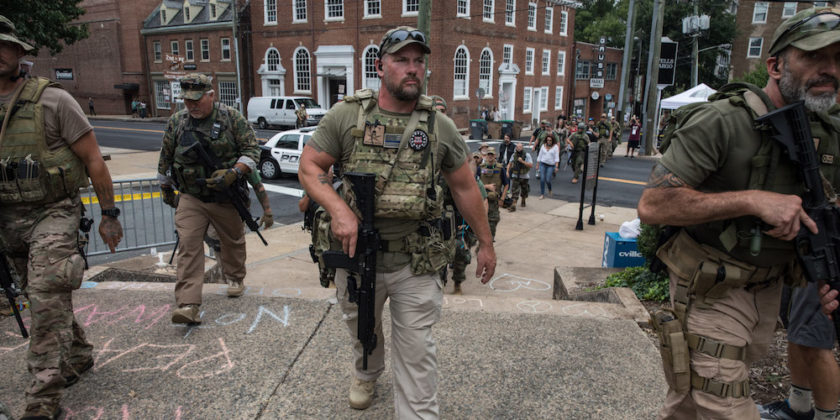
Militia men in Charlottesville Virginia, 2017.
The combination of anger at the government, fear of gun confiscation and susceptibility to elaborate conspiracy theories is what formed the core of the militia movement’s ideology. Although there were white supremacists in the movement, and although groups and individuals within the movement often made common cause with or at least tolerated hate groups, the orientation of the militia movement remained primarily anti-government and conspiratorial (ADL website).
Far right militia groups in the United States are diversely constituted, made up of libertarian as well as a diverse array of Ethno-nationalist and Nazi affiliated groups. Many militia groups see themselves as legitimate organizations with legal standing, as authorized by constitutional and statute law, particularly where state and federal law cite legitimate roles for an “unorganized militia.” Others take a different view, making claims on the basis of what sometimes called “insurrection theory,” which describes the right of the people/body politic to rebel against the government in the face of tyranny. These groups remain firm in their conviction despite the legal precedence set by the 1951 case Dennis vs. the United States. In this decision, the U.S. Supreme Court rejected the insurrection theory, stating that as long as the government provides for free elections and trials by jury, “political self-defense” cannot be undertaken.
In 2016, the Southern Poverty Law Center identified 623 anti-government groups that were active the prior year. Of these groups, 165 were militias and the remainder includes “common-law” courts, publishers, ministries and citizens’ groups. This represents more than a 30% increase over prior years. The antigovernment movement, according to SPLC, experienced a resurgence for reasons that attributed to the 2008 election of President Obama, the nation’s first black President. This combined with a struggling economy and changing demographics driven by immigration have helped foster growth of the movement.
Antigovernment “Patriot” groups define themselves as opposed to the “New World Order,” engage in groundless conspiracy theorizing, or advocate or adhere to extreme antigovernment doctrines. Antigovernment groups do not necessarily advocate or engage in violence or other criminal activities, though some have. Many warn of impending government violence or the need to prepare for a coming revolution. Many antigovernment groups are not racist. And it is worth emphasizing not all anti-government roups are constituted as militias.
Militia men in Charlottesville Virginia, 2017.
Anti-government and militia groups include a diverse array of organizations that include the Oathkeepers, the Three Percenters, Arizona Border Recon, Hutaree, Fraternal Order of the Alt-Knights, Kentucky State Militia, Ohio Unorganized Militia Assistance and Advisory Committee, Southeastern Ohio Defense Force, Michigan Militia (two factions using the same name), Southern Indiana Regional Militia, Southern California High Desert Militia-and many others. In Pennsylvania, there is the Pennsylvania Military Reserve, the Berks County Patriots, and the Western Pa Liberty Forum.
For a more behind the scenes and intimate look at militia groups, check out the video (produced by Vice Media) on the Three Percent Movement.
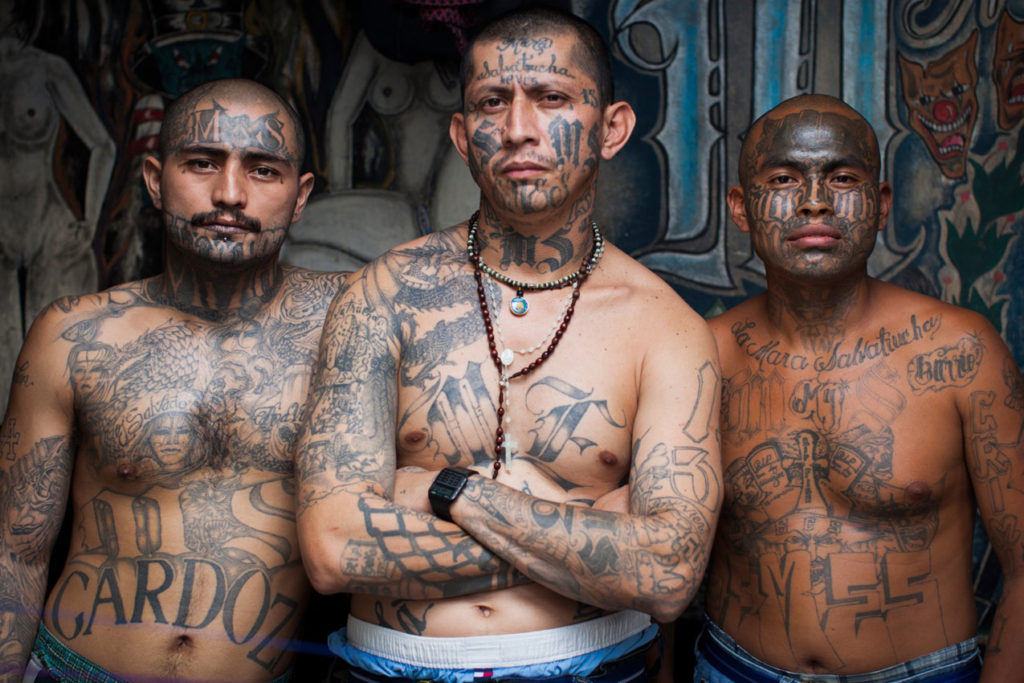
Gangs – MS-13
While technically not affiliated with protest movement politics, politicians have recently pointed to MS-13 – an international criminal gang – in their efforts to create a spoiled identity for rival politicians (i.e. 2017 Gillespie vs. Northam race in Virgina).
Originally based in the refugee-swollen neighborhoods of 1980s Los Angeles, the gang spread across the United States, Mexico, Canada, and throughout Central and South America. It is not strictly an urban phenomenon, as its members are diffused throughout the social landscape.
Ethnically speaking, many of the members identify as Central American and, to be more specific, Salvadoran. Their activities have gone a long way in establishing what in Central America is referred to as the “Northern Triangle” – Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras — as the most violent place in the world that is not at war.
In the U.S., the highest concentration of gang activity in California, followed by Washington D.C., Houston, New York City, New Jersey, and Boston. Members are known by their distinctive tattoo markings include “MS”, “Salvatrucha”, the “Devil Horns”), their own gang sign language, and, of course, for their violence.
Minors make up the majority of suspects arrested for killings attributed to MS-13. This has caused many schools, particularly those located in the southern parts of the U.S., to admit students who arrive unaccompanied in the county with caution (and in some cases not admit at all). Whatever the case may be, the lone status of the children potentially leaves them vulnerable to gang recruitment, even if they were unaffiliated upon arrival.
Though their historical roots lie in Central America and the cities of the United States, much of the recent growth of the MS13 has been concentrated in Mexico. The gang is strongest in the border region with Guatemala, especially the state of Chiapas. Drawn by the tens of thousands of Central American migrants seeking illicit passage through Mexico to the United States, MS13 has developed into one of the foremost players in the nation’s thriving human trafficking industry.
Why Hate Speech is Not “Free Speech” (re-blog from George Lakoff)
Like violence, hate speech can also be a physical imposition on the freedom of others. That is because language has a psychological effect imposed physically — on the neural system, with long-term crippling effects.
Here is the reason:
All thought is carried out by neural circuitry — it does not float in air. Language neurally activates thought. Language can thus change brains, both for the better and the worse. Hate speech changes the brains of those hated for the worse, creating toxic stress, fear, and distrust — all physical, all in one’s neural circuitry active every day. This internal harm can be even more severe than an attack with a fist. It imposes on the freedom to think and therefore act free of fear, threats, and distrust. It imposes on one’s ability to think and act like a fully free citizen for a long time.
That’s why hate speech imposes on the freedom of those targeted by the hate. Since being free in a free society requires not imposing on the freedom of others, hate speech does not fall under the category of free speech.
Hate speech can also change the brains of those with mild prejudice, moving it towards hate and threatening action. When hate is physically in your brain, then you think hate and feel hate, you are moved to act to carry out what you physically, in your neural system, think and feel.
That is why hate speech is not “mere” speech. And since it imposes on the freedom of others, it is not an instance of freedom.
The long-term, often crippling physical effects of hate speech on the neural systems of those hated does not have status in law, since our neural systems do not have status in our legal system — at least not yet. This is a gap between the law and the truth.
George Lakoff is the Richard and Rhoda Goldman Distinguished Professor of Cognitive Science and Linguistics at the University of California at Berkeley, where he has taught since 1972.
Should Protesting Have Limits? Should it be Criminalized?
Although the First Amendment guarantees free speech and protects political protests, this guarantee is not absolute. The government can and does enforce stipulations that it considers reasonable; restrictions over time, place and manner that a peaceable protest can take place. The key here, it was pointed out, is – What is reasonable? How does one negotiate the fine line between what is reasonable and lawful and what is unreasonable and provocative? And therein lies the problem.
Sources
Washington Post article , by Hawkins
Ciccariello-Maher, George (2017). Decolonizing Dialectics. Durham, North Carolina: Duke University Press.
Unmasking the Blac Bloc: Who They Are, What They Do, How They Work
Anti-Defamation League website
“Just How Much Can the State Restrict a Peaceful Protest,” by Braden Goyette ProPublica website
“Flags and Other Symbols Used by Far Right Groups in Charlottesville,” SPLC website
Why Hate Speech is Not Free Speech, by George Lakoff
“When White Nationalist Shout Their weird Slogans What Do They Mean?” by David Niewert, 2017.
Questions
Have you ever participated in a political protest?
Have you ever been “inconvenienced” by a political protest?
Do you think political protest should be criminalized?
Do you ever find it ever to be the case that you support absolutist interpretations of the 2nd Amendment of the U.S. Constitution (resisting interpretations that propose controls on gun ownership and access to weapons) while at the same time you do not hold similarly absolutist views when it comes to 1st Amendment rights? If that is indeed the case, how do you explain the contradiction in thinking?



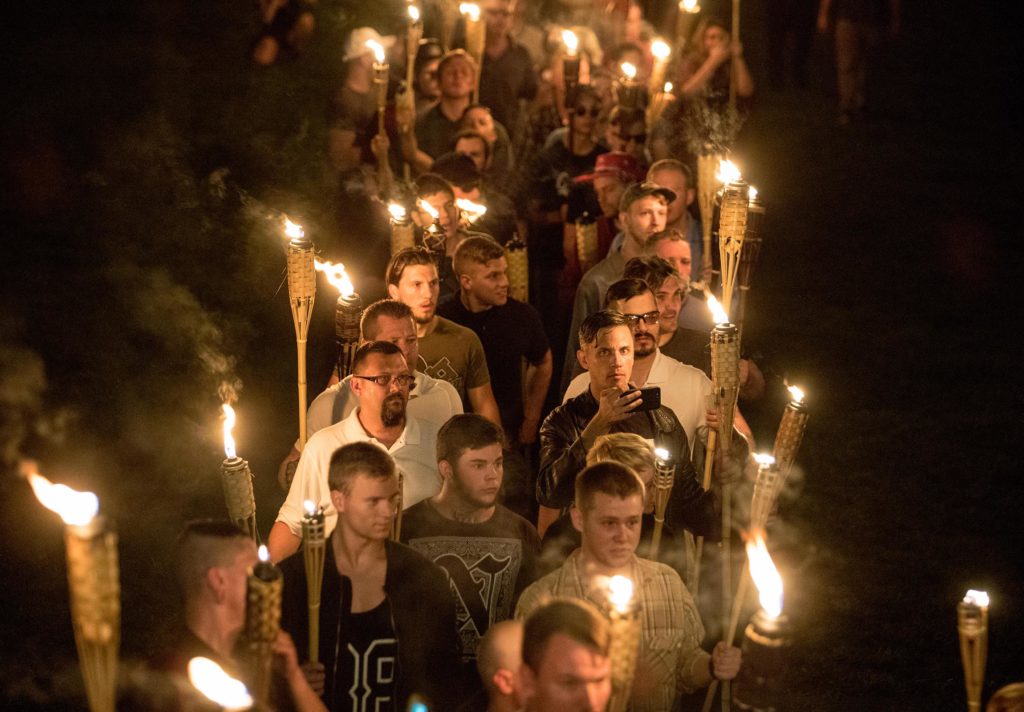





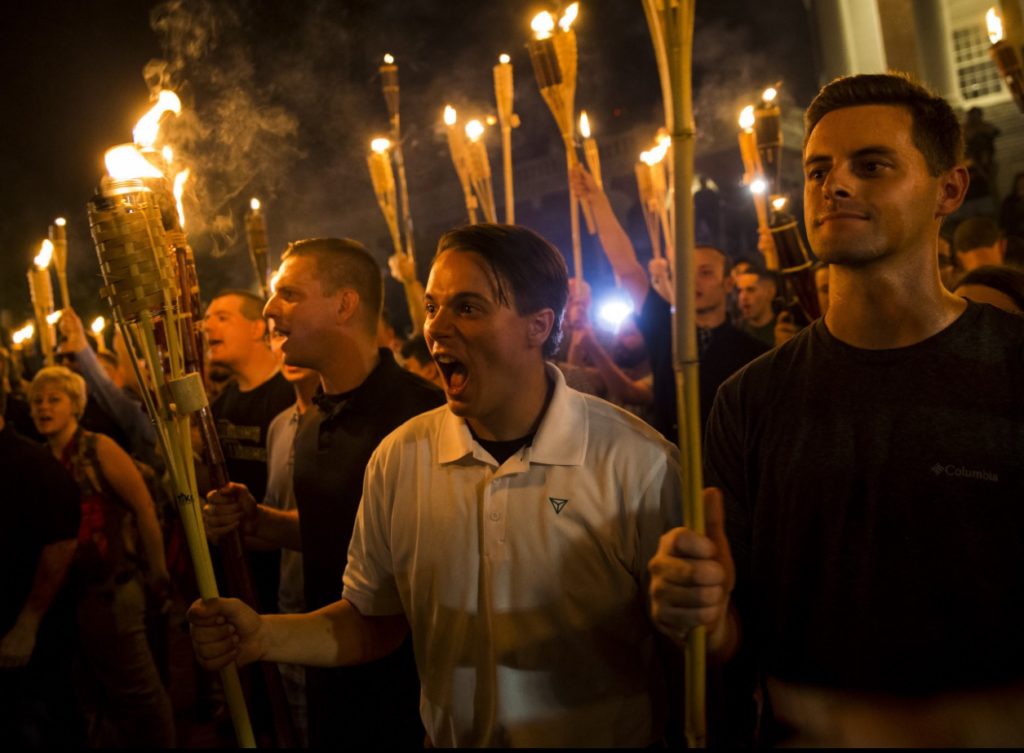

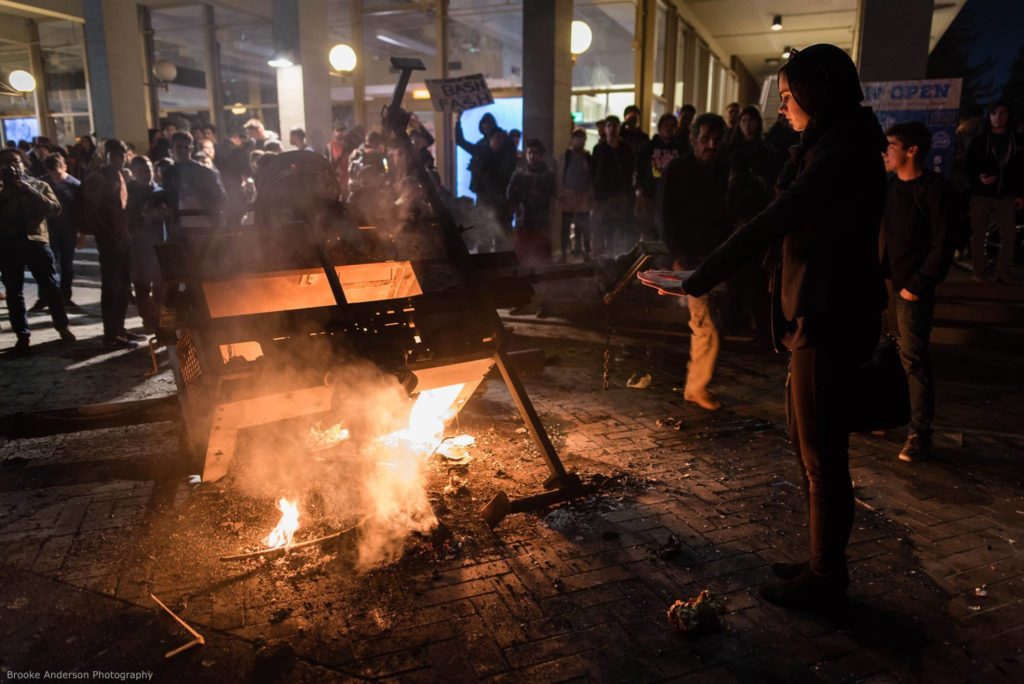






I personally have never been to a political protest, I have just seen them on the news and heard about them. However, I do not think that they should be ciminalized because It is a way for people to express dissatisfaction with current situations and assert demands for social, political, and economic change. It is also apart of the first amendment and should not be taken away unless there are serious issues such as violence.
Even though there are countless number of protests occurring on different political issues, I can say that I have not participated in any. If there was one that I supported, I would give my support from a far rather than getting caught in the crowd. I remember two years ago in Philadelphia there were multiple protest regarding the Black Lives Matter situation that I wanted to be there for. Most of my friends, even my aunt, participated in the protest and weren’t afraid of what could possibly happen. Even though I wasn’t involved physically in the protest I still tried to give my support. Personally, I can’t see myself physically protesting but will try and help in other ways. I do not think that political protest should be criminalized at all. Knowing that many protests can get out of hand and violent, they should be carefully watched or looked over. An example is when the White House was marched on back in January 2021. Like every protest, this one began normally and then escalated quickly when the protesters broke into the building and acted as if it was a playground. So no, protests should not be criminalized but controlled to prevent disorder. Obviously not all protests should be acceptable, but there are some that have shown to have good reason behind it.
There were many times when I felt very opposed to particular political protests that were taking place. Undoubtedly protests that oppose my own political beliefs. I think everyone should be able to politically protest. Although I have never participated in one, there have been protests that I wish I had. The first amendment guarantees everyone the right to freedom of speech. Protests are carried out in an effort to persuade others to take a position and effect change. People engage in this activity in an effort to have their voices heard and to be noticed by the government. Never once have I considered making protesting a criminal offense. I think it’s a method for people to unite and fight for the same cause. People’s protests have resulted in some changes to certain things. For instance, when Trump was elected as president, the Women’s March on Washington had around 470,000 people walking in support of women’s rights. At least 25 separate women had alleged sexual misconduct against Trump. More than 600 marches were scheduled in the United States, and the protest received enormous support from throughout the world. Another example is Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech, which was delivered during the March on Washington. This protest took place in August 1963 to support racial equality in the US. More than 200,000 people attended in harmony. I think we should maintain our right to protest and not be punished for it because there have been several protests that have significantly changed our world.
The social disorganization theory is a way of thinking about crime that explains why crime rates vary depending on the structural and cultural elements that influence how people interact. People who live in socially unorganized neighborhoods are frequently in need and lack the resources to protect themselves against crime. I believe that some concepts or methods should need to be implemented since they can most effectively benefit the neighborhood’s youth. Children are more likely to have weak bonds to traditional society in societies where there is a lot of social disruption. Children will find it simpler to make friends with a bad crowd in these circumstances, increasing their likelihood of becoming involved in crime. According to the social disorganization theory, a person’s neighborhood has a greater impact on their likelihood of committing a crime than their personality. Therefore, if a child grows up in a poorly governed society, it may have an impact on how they develop and what they choose to do with their lives. Children should be our first concern since they are our future. When they don’t have any, children should have free access to resources and counseling.
Despite how opinionated I am on various vital issues within the sphere of American politics, I have never participated in a political protest. Having said that, there have been multiple occasions in which I’ve wanted to be involved, the most recent of which is that of the protest at University Park. Referring to the article, allowing highly provocative groups on university grounds like the Proud Boys under the guise of “free speech” advocacy should not be tolerated, as hate speech in no way qualifies as permissible free speech. Depending on the message of the specific protest, I am often not inconvenienced by political protests, something that I’ll openly admit illustrates privilege. To elaborate, some of the protests within the past few years have revolved around ideas and goals that I stand by (i.e., restrictions of police funding and restructuring policing nationwide, the fight for civil rights and equal representation of people of color and women, and the access to public and higher educations). On the other hand, many have preached a message of hatred and dogmatism. Unfortunately, it is the latter of which that I have never been the victim or target of; as a white male, I am privileged to not have been the target of protests like the Unite the Right rally. With that said, I can still be cognizant of the threat that the alt-right poses to many within the country and act in defense of those targeted by such bigotry. The notion of criminalizing protest is quite a nuanced and difficult topic to discuss. On paper, it would be ideal for a democratic society to have the ability to openly exchange ideas and concerns civilly, thus allowing for the careful and critical analysis of problems affecting the country. In practice, however, we have witnessed many escalate into altercations and violence. Having said that, I am of the opinion that political protest should not be criminalized, but rather limited and regulated to prevent violence. Where I would draw the line, however, is when the message of said protests is that of neo-fascism and classic American white authoritarianism, supremacism, and nationalism. Ideas like these are of a draconian, less enlightened, and tolerant era; as such, they should remain in the past to serve as something to learn from and admonish. The absolute freedom of the second amendment is a myth and something I personally disagree with. As with the first amendment, there should be logical and evidence-based limitations to the right to bear arms, arguably to a greater extent. Our ability to use speech to convey ideas is powerful and has tangible effects on society. With such a power, death and destruction, while certainly possible, are less frequent. With firearms, it is ostensibly far easier to sow chaos; thus the need for limitations is evident.
I have never participated in a political protest, but I remember some protests in the past in the United States and Puerto Rico. One protest that I remember clearly happened in Puerto Rico that arose to remove the governor. This was because the information had leaked out that he was stealing money from the people. I did not participate but I had friends who did, and the way people express themselves in a protest is opposite. Some people stick to the style of attacking and vandalizing, painting walls, and breaking glass. While other people prefer to protest differently. In this protest I am talking about, you saw everything from people protesting doing yoga to people dancing and singing. I remember that it became a meme “perreo combative”. People were not protesting because they wanted an unreasonable person out of office but because he was a corrupt person who was hurting the people. Artists like Bad Bunny and Residente traveled to march with the people, and I think it’s impressive how people who probably don’t agree with anything can come together for a common struggle. I think that’s one of the protests I would have liked to participate in because I think it was for a good cause. I have not yet had the opportunity to see a protest in the U.S. being here although I have heard and read about the gun rights protests which are protests that I think should be heard considering the problems that guns are causing with school shootings.
I have participated in one political protest, and it was in my hometown after the murder of George Floyd. It was a racial inequality protest due to the amount of racism present in the community I grew up in. It was a peaceful protest, as there were no ill intentions by anyone who created the protest, or anyone who participated. Although there were no ill intentions and it was made known of that, there were still community members following us all around downtown Elizabeth with handguns and AR-15s “in preparation to protect the surrounding businesses” (businesses that they did not even own). It was actually mind blowing to me, and just made these people who followed us with guns look like cowards; why did they want to have the opportunity to shoot someone? What would their reasoning have been for killing someone when arrested? I had so many questions surrounding what reasons they had for this besides the fact they did not agree with our protest and were part of the reason we were protesting to begin with. I have never been “inconvenienced” by a protest in my eyes; some roads have been closed down because of them, yes, but I never saw it as an inconvenience, I just viewed it as the road was being used and I had to go a different way. I do not think political protests should be criminalized, I do think violence within political protests should be criminalized in order to protect people in the future who were to protest for different reasons.
I have never been involved in a political protest and I don’t think that I ever will be a part of one, just because I cannot see myself doing that with my anxiety and all that going on in one place. Like the one we talked about in class this week in regards to the speaker at Penn State. I do not believe they should have even accepted a known violent group to speak at the university. But I also could not be one of the ones shouting at the troopers. Seeing those videos that we saw during class off of twitter just made my heart race let alone me being there. I also do not think I have ever been inconvenienced by a political protest, I think the closest I have ever been to one first hand was the one in Italy were they started protesting down the street that we were on. I am also not one to believe that they should be criminalized, I think they are useful and help others feel better about getting some feelings off their chest. I think some groups that are hateful and are also violent protestors should be criminalized. Because how is it you have to violently get into something at a protest to get inducted into said group.
I’ve never taken part in or been inconvenienced by a political protest. There have undoubtedly been political protests that conflict with my values, but that is the only way that it could bother me or change my ideas. Every American citizen, in my opinion, should have the right to freely express their opinions in public and alongside like-minded individuals. It should not in any way be made a crime, in my opinion. People typically engage in peaceful protests to demand change and to be heard. I don’t see anything wrong with peacefully expressing your opinions, your desires for change, and your plans for the future. Our society is formed as a result of how we express our ideas and strive for change. Yes, there have been protests that have worsened circumstances, but we must examine why that happens. For instance, after George Floyd was killed, a lot of people protested and the “Black Lives Matter” movement was born. Many nonviolent protests were unjustly blasted with tear gas. There are groups of people who are already so overcome with anger, fear, and grief that they only want to try to change the world and feel heard by those who share their strong beliefs. In response to your question, protests shouldn’t be made illegal, but we should consider the causes of inappropriate replies instead. The question of whether or not to make protests illegal should never be asked. What are the factors that contribute to “peaceful” protests labeled as criminal activity?
I have never participated in political protest, but i do remember seeing a lot about them in past years and even now sometimes. I can’t say I’ve ever seen a protest in person or even seen one from afar. I don’t think protest should be criminalized until they start causing harm to people or surrounding buildings. For me personally I do think there could be better background checks for guns and who can have them, but I do agree that some people should have the right to bear arms. The right to bear arms is a serious thing and should definitely be consider a tougher background check and you should have to show more requirements in order to carry one. If you show the said requirements and show you are able to carry then there is no problem with having this amendment in place for people to carry guns.
– I personally have never been involved in a political protest, nor has a political protest every affected me in anyway. I do not think that political protest should ever be criminalized if they are peaceful. I believe it is a right in America to be able to protest the government but if they ever become violent, I think then it can be criminalized. People sometimes don’t know how to control themselves so when a protest is going on and there is a lot of people, and it is an important topic or situation going on people sometimes go to committing crime like vandalism and destroying things. And at that point I think it’s fair for someone to be criminalized. One issue with protest in the US is some of the time when a protest is happening, it is when the police did something harmful to the community, so it does not go over well when you are doing a protest and the people who are supposed to be looking over the protest, is the same reason you’re protesting in the first place. People don’t trust law enforcement 100% of the time so when they try to stop you it becomes a major conflict and I think that is when crimes start happening. It is your first amendment right to have a protest whenever you want, but as I stated never should it become violent, or you will be criminally prosecuted.
Do you think political protest should be criminalized?
Political protest should not be criminalized. Politics and opinions on them lie within our first amendment right. Expressing opinion, disagreement, need for change, etc are all crucial in how a society evolves. While different forms of protesting may lead to different outcomes, it is non-violent protesting that cannot be widely criticized in a negative sense. Violent protests are judged by the public and harmful to the welfare of a community. They ask so seem to give a bad name to all protests themselves. “Non-violent techniques of protest include boycotting, sit-ins, picketing, marching, and the nonpayment of taxes” (para 5). Non-violent techniques might not work as fast or show immediate severity, but they ensure safety and less hostility between the public and law enforcement. “There is a fine line to negotiate between free speech and disorderly conduct. Many protestors have argued that they were arrested for simply passing through an area or for standing on a public sidewalk” (para 7). The hostility and distrust between the public and law enforcement shows hindrances that affect peaceful or passive acts, given a misconception or a formulated opinion. Combatting this may find a solution in peaceful tactics of protesting. It is then for the public eye to see the true intention of change, and if met with force, that it was not started by the protest itself. I see it as building trust and making a better reputation for protesting as a community, and also to put stop to blame for why societal change will not work a certain way.
In my personal opinion, I do not believe political protests should be criminalized. Political protest refers to actions taken by individuals and/or groups to address or end perceived injustices in a political system. Civil disobedience, a nonviolent method of political protest, is the refusal to abide by laws that one feels are immoral. These demonstrations aim to create a spectacle in public and draw attention to a particular problem. They typically take the form of passive resistance and are nonviolent. Boycotts, sit-ins, and other nonviolent forms of political protest are a few examples. Protesting is a form of free speech that has recently become the subject of controversy. As some locations now require a permit to protest, our First Amendment rights have now been restricted. This promotes equity so that all groups can use the site, despite the fact that protests are intended to be disruptive and provocative. Many different people and/or groups protest for a variety of reasons. Antifa advocates utilizing all available measures to fight capitalism, fascism, and white supremacy. They are anti-facism. Nazis (American) are attempting to resurrect and reestablish Nazi ideology. The alt-right is a group of far-right, anti-Semitic movements that promote white supremacy. Black-boc, is a tactic that acts as ad hoc assemblages that last the duration of marches/rallies. The goal of the Rise Above Movement (RAM) is to restore Western manhood. Lastly, militias and anti-government organizations harbor animosity toward the government and have fears about gun confiscation and have a tendency for believing elaborate conspiracies theories. With that being said, I do not believe political protests should be criminalized. Even if those opinions are morally repugnant to me or others, everyone has the right to express their opinions without censor or restraint. What I do believe should be criminalized is the use of hate speech. Free speech does not include hate speech. Like violence, hate speech has the potential to physically restrict others’ freedom. This is due to the psychological impact language has on the brain system, which can have permanently debilitating implications. Hate speech causes harmful stress, dread, and distrust in the brains of the people who are being spoken about. Even worse than a physical attack, it can be the internal damage. It restricts one’s ability to think freely and, as a result, to act with worry, danger, or mistrust. For time, it restricts one’s capacity to think and behave as a fully free citizen. Hate speech is therefore not “mere” speech. Additionally, it is not an example of freedom because it restricts the freedom of others. Political protest can be a means of expressing one’s opinions and beliefs, but I think it should be criminalized when it results in violence against other individuals and is outright just hatred speech.
I AM ALL FOR PROTEST! It can get very complicated though. I attended the George Floyd protest in Pittsburgh and it was wild. I know usually people always say that they are down with the protesting, but not the violence, but I am down with all of it. The looting I saw, the police vehicles being set on fire, windows being smashed. I feel like sometimes people need to see scenes like that to make it real for them. Black people have protested by use of marching, sit-ins, boycotts, kneeling, and nothing seems to work so how can you be upset when stuff gets turned up a notch. On the other hand, I am conflicted when it comes to the white supremacy stuff. I am from Virginia, and the weekend of the Unite the Right rally in Charlottesville, I was supposed to be attending a concert out there that got cancelled because of the rally. I’m all for free speech until hate starts to spew out. Just like it said in the article, hate speech is not free speech. The words you speak do have power. I think any large congregation of white men scare all of us, especially Black people.
I also thought it was interesting how the article brought up how the city of Charlottsville is a monument for white supremacy. The city I’m from is like this (Fredericksburg, VA). The neighborhood I grew up in is named Lee’s Crossing after Robert E Lee. My street address was Mcclellan St after a confederate general, and our major highway named Jefferson Davis HWY after more confederates. There was literally an old slave block on the sidewalk downtown. Once protest sparked all over the country after the death of George Floyd, it lighted a fire in my hometown too. Protests to get the slave block removed, protests to get our highway renamed and etc.. So in that light, I think protest is great. It’s inspiring, and it reminds us that we the people do have power, even if it doesn’t seem like it. Also, I can not believe some of the other comments on here.
I think it’s interesting how people hyperventilate about violence directed at private property, but when that violence is directed at the bodies and bodily autonomy of actual human beings in the form of direct (interpersonal) and indirect (structural) violence, they don’t demonstrate similar outrage. Actually, many of them are not outraged in the slightest.
I personally have never been in or to a political protest, but I’ve seen it on TV and stuff like that. I’ve never been in a political protest because I just don’t want to be in a situation like that because I know sometimes they get a little crazy.
Political protests should not be criminalized unless they become violent. It is a way of trying to prove a point, or show a message. The 1st Amendment is one of the most important Amendments and should not be taken away, especially in situations like this.
I believe that both the 1st and 2nd amendment are very important. Some people feel better with a voice rather than a gun or the other way around. Taking those two big things will only make the problem worse. If the protests get violent then I understand why taking these would be okay, but people aren’t doing much right now so the government needs to back off a little.
I have never participated in a political protest. Mainly because they do not interest me and i am not the kind of person to do so.
Political protest have not inconvenienced me in my everyday life but i have been handed flyers about protest while walking around and i usually just take it and throw it away.
They should only be criminalized if they are messing up peoples everyday lives, like messing up traffic
I personally have never been in or to a political protest. Not because I don’t stand for the topics that are being protested, but mainly because I don’t want to put myself in harm’s way. It sounds a little selfish because most people would say if you’re going to support the cause you have to do everything you can to help. I do understand that and where they’re coming from but I just believe there are things you and do and protesting just not being one of them for me.
I have never been inconvenienced by one, but my aunt lives in D.C and she was never big on protesting. She finds it a waste of time, and would rather be out doing other things. When she’s walking through the city although shes constantly running into protests and she never starts again thing with them, but she says sometimes they try to follow her and continue to talk about their cause when she has to be at work so for her it’s a major inconvenience.
I don’t think that it should be criminalized, but I do think that something needs to be done. People are getting harmed and killed at them. Which is, in my opinion, no way to have your life ended. Precautions need to be taken by the protestors. People will never stop protesting, if you tell them they can’t protest then they’ll protest that they can’t protest. Criminalizing it just isn’t the answer I believe it will just cause more problems.
.
I personally have never been in a political protest, or a protest of any kind for that matter but I do believe in the right to protest. The right to protest is essentially an extension of the right to freedom of speech. However in recent years that right has been abused. Many groups claiming to be peaceful have rioted and broke out in violence during protests. At a certain point protests can go to far by endangering peoples lives and at that point I would consider criminalizing protests. If the protest is not causing any harm to people or property then I support the right to continue this form of protest. This may only be my opinion due to the fact that I’ve never been inconvenienced by any political protests. I also believe that just as protests should be permitted so should the second amendment be permitted. My family has always supported this right and exercises our freedoms permitted by it.
Personally, I’ve never participated in a political protest or any form of protest myself. Even though I’ve never been in a protest, I have witnessed and have been inconvenienced by a protest just this past summer, when President Trump passed an executive order to ban travel restrictions to certain countries of the world. Unfortunately my family and I were stuck in traffic for hours due to the Travel Ban protests that were taking place at Philadelphia Airport.
In my opinion political protest should not be criminalized. I believe that our First Amendment of Free Speech should never be criminalized unless protests were to revert from peaceful to violent. For instance, short after Trump won the presidential election, protests broke out in chaos. In these form of “Violent Protests”, the protesters were vandalizing stores and vehicles in sight. These form of protest should be prevented and stopped using all means necessary.
I have not personally participated in any political protests. I have never been involved or effected directly and I do not think I will ever be in the future. I am never one to stand out and speak my voice, but rather listen to what people have to say from all sides and then give my final thoughts if asked.
When the whole “Black Lives Matter” movement was started people always asked me if I was going to be involved in the marches. As i stated I do not like to be one of the people who stand out so I would always say no but at times I would feel uncomfortable. I would overhear people saying either negative comments about the movement or positive things and I would just sit and listen to their thoughts.
I believe that the first and second amendments are essential to this country. They were included in the constitution for reasons. I do and will support people practicing the first amendment until they try to abuse it as well as the second amendment.
I have not participated in any protests myself but I know people that have. I personally don’t have much opinion on protesting being that I’ve never really experienced it. I am from Pittsburgh where there have been a number of protests. These demonstrations though, have not gotten in the way of the populations day to day life. From what I’ve read about these acts of civil disobedience I have formulated the opinion that everyone is entitled to stand up for whatever they believe in as long as is doesn’t cause disruption or harm to anyone involved or nearby. Protest should be controlled to an extent to which they don’t turn into riots but not so much that the demonstrators cannot get their point across.
All in all, civil disobedience should in no way be criminalized. Doing so would be in fact unconstitutional. Though it shouldn’t be criminalized is should definitely be under control to prevent disruption or injury.
I have never personally partaken in a protest nor have i ever been inconvenienced by one. I have seen protests through pictures and videos.
I don’t believe that protests should be criminalized unless the protest causes a lot of damage and injures people.
On the topic of supporting people with guns and the second amendment, i do believe people should be able to bear arms but for people to be able to bear multiple fire arms they should have persistent checks.
I have never participated in any sort of protest and probably never will. The reason for this is because I don’t have the time, nor do I feel like wasting other peoples time. Even though I will not participate in any kind of protest I do enjoy watching certain videos on YouTube of protesters
I have never been inconvenienced by a protest, probably since I live in Amish country and I don’t think they are going to protest about anything in the near future.
I do think public protest should be held to the same accountability of the of someone who is not protesting for example. if you are blocking the road and the police tell you to move, just listen because if refuse then you are breaking the law. another being if you are in any way harming someone or destroying property then you should be held accountable and charged since protesting does not put you above the law.
sometimes I do find myself on the side of people fighting for their second amendment rights, but to an extent since most of the time they turn out to be insane. same goes for the other side they can be just as nuts and also really annoying.
For what I think of the second amendment is that you can carry what ever you want as long as you have a permit. But I believe that restrictions fully automatic battle rifles should be available to the military(not police) unless you have the right licensing to own one, and are only allowed to shoot them on a range that allows them. The way think of the second amendment is probably the reason I see these protests as I do and why my thoughts on the matter is kind of one split but leaning to one side
No, I have never participated in a political protest, but I feel that it is mostly due to the fact that I’ve never really been presented the oppurtunity to participate. I have also never been directly inconvenienced by such political protests, but Im sure there have been cases where I was not aware of such inconveniences.
I feel that political protests should not be criminalized as protesting is one of the primary ways to spread awareness of injustices and allow for progress to take place. I also agree that there is an extent to this amnesty, as with political protests that travel beyond the boundaries of peaceful protest and lead to violence, then those that partake in such activities should be dealt with as criminals.
The 2nd amendment is one of the most controversial topics in the last couple decades. I feel that regulations and restrictions need to be in place to allow proper screening and prevention of guns being legally sold to those that are determined ill fit to own a firearm. Of course people assume that these guns will find their way to people via illegal means but that is a separate matter that the police must deal with. I feel like anything more than a semiautomatic pistol (or something similar) is pushing it when it comes to personal defense. Especially in regards to the fully automatic/ burst fire weapons that should be without a doubt banned from civilian purchase. In regards to the 1st amendment, I feel that although it sounds like a good idea to be an “absolutist” on this, there should be restrictions when it comes to hate speech and other derogatory manners.
I have never been involved in a political protest before, but I would say the media has done a very good job at letting us see all of the protests around the country and the world. I have not been inconvenienced by a protest either, but in that situation I know I would be annoyed. However. it is always good to look at the big picture and try to get a sense of what people are trying to say.
Criminalizing political protests would be a huge mistake because it would be counterproductive of our politicians. How will the issues of the people be solved, if the voice of the people is silenced? How will they be listened to if they don’t grab our government’s attention? That is exactly why the line is crossed at many protests we hear about. The attention of our politicians is not centered on those who are passive. It is centered on those who are violent and are willing to break the law in order to be heard. Breaking the law is a quick way to get attention from the media and the government. I do not condone it, but it is simply how our system works.
I believe that the first amendment should always stand because it is what makes our country a representative democracy. America exists today because people got tired of not having that right. I am not hater of the second amendment, in fact, I believe everyone should have the right to own a gun if they want to defend themselves because it is what our constitution says. However, after seeing a tragic event like what happened in Las Vegas, it is very tempting to say that the second amendment should be abolished, but that should never be the case. I say that because it would be the beginning of our country’s second Civil War. In all seriousness, I do not believe that everyone’s right should be taken away simply because of someone’s improper use of a weapon to harm others. It is that same reason why many will argue the second amendment exists. The truth is: people are using guns to kill people. After massacres like Orlando and Las Vegas something has to happen in regards to how we control gun violence in America.
I have not been apart of a political protest.and do not plan on being apart of one. In my opinion they seen dangerous as other people will get angry at you for taking up their time or police may get violent.
I do not believe political protests should be criminalized as they are speaking out about an issue. As long as they stay peaceful they should be allowed to protest in public.
I believe that the first and second amendments should not be tampered with. These two amendments allow people to protect themselves physically and verbally. They can speak out against the government when they do something wrong and they can protect themselves when they are in danger. I never believe the first amendment nor the second amendment should be changed in any way.
I have not involve in any types of political protest neither in my hometown, China, or here in America. But I have seen many small protests on the streets. Before college, I spent my four years of high school in the orange county of California, and for many times I saw people gathering on the street, holding boards, giving small speech, and separating posters, and most of the protests I saw was for save water and keep environment nice.
I do not think political protests is criminalized as long as they cause no harm to surrounding people or severe outcome to the country. Since the first amendment gives all people the equal rights on freedom of assemble and speech, we should keep it.
I support the first amendment but not the second amendment. The first amendment gives all citizens the equal rights on freedom, it is important for people to show their needs from the government and can tell suggestions. For the second amendment, I accept it but never support it. Guns can be used both for protection and causing harm, so a heavy control on weapons and background checking are significantly necessary.
No, I have never participated in a political protest, but I have witnessed several in my hometown. The political protests that I have witnessed were peaceful protests, never violent protests.
No, political protest has never been an inconvenience to me personally. Although I have never participated in one, I do not have a problem protesting, and I have noticed that it can make a positive difference when one protests.
No, I do not think political protest should be criminalized because in the United States we the people have freedom of speech. The right to speak freely allows us to have opinions without interference of the law.
The views I have between the 1st and 2nd amendment is similar. I do believe in the 1st amendment (freedom of speech) as well as the 2nd amendment (gun ownership and access to weapons). As long as they are properly enforced I do not feel like there is a contradiction between the laws that will interfere with political views.
I am not sure if you would consider it a political protest, but I did go with my dad to a protest in Washington D.C in front of the Supreme Court. All we did was walk around the block a few times while some people were reading from the Bible. I don’t really feel comfortable explaining what the protest was for because I didn’t totally agree with it, I was there to support my dad.
I have never been “inconvenienced” by a political protest and the one I participated in was not “inconvenient” for anyone else. There was a different kind of protest in the form of a very fun and colorful street party in Washington W.D that same day I was there, which was in celebration or protest of what I was there for. I would say maybe my dad thought that was an inconvenient for him though.
Some protests get way out of hand and I do not agree with those. Therefore, if people are being violent and destructive, that should be criminalized. If it is just a get together to vocalize opinion/feelings, then that should be okay. I don’t think a protest party should force their opinions on others where it affects other peoples lives who just want to get somewhere, but they can simply get their point across.
I think people should have the right to purchase a gun, but I think there should be a process for people to get them. We take a test to get a drivers license, why can’t there be a test to be able to obtain a gun. It may help keep weapons out of the wrong hands. At the same time though, guns are traded and bought out in the streets. So honestly, I have no real idea or opinion on this topic.
I have not personally participated in any political protests. Whilst I’ve never been impacted or effected directly, I think everyone here at least been minorly inconvenienced in the form of how goods flow. i.e. deliveries from amazon, or even deliveries via truck that would happen to get delayed due to protests happening in streets and highways.
Protests should not be criminalized. People who infringe on the laws during these protests are the only ones who should be punished. With that being said, protests that turn violent should be met with militaristic or police force with the goal of maintaining the peace and reducing the overall amount of damage and harm that would occur. People that are detained during this time, if suspected in taking part of these activities should be prosecuted. Of course people who weren’t doing anything illegal would inevitably be caught up as well. If they weren’t doing anything wrong, the likelihood of these people being prosecuted is, in theory, relatively low. With that in mind, is it better for protests to devolve into riots? Or is it better for a few innocent people to be detained in the goal of keeping the peace, and possibly even preserving human life?
I believe that the first and second amendments are essential to this country. They were included in the constitution for reasons. I do and will support people practicing the first amendment until they try to abuse it in such a way where they can break other laws. As someone who exercises the second amendment, I believe that the second amendment shouldn’t go anywhere.
I personally have never participated in a protest. Although I do believe they are great fro getting a point across and showing what your moral values are through what ever it is you at protesting against. As far as i can remember i have never been inconvenienced from a protest. My personal belief would be that no one should be inconvenienced by a protest because it should all be peaceful protest.
I believe that peaceful protest shouldn’t be decriminalized because it allows the people to gather as one and share their voice as a greater mass. In regards to this I also believe that there needs to be strick laws that outline the difference between peaceful and destructive protest. I say this because i have witnessed many protests that have gone violet and there being no reprimands for the destruction that was caused.
My family and I have always supported the second amendment because we believe the government is responsible for protecting the government and the land of the United states and we are responsible for protecting ourselves as individuals. As far as the first amendment I believe everyone has the write to speak their mind as long as it doesn’t infringe upon others safety.
Have you ever participated in a political protest?
-No, growing up in a small town I could not take part in anything off a large scale, but even smaller protests at school and in town, I never really had a burning passion to take part. I have my beliefs, my codes, but I prefer not to get involved and make my own beliefs everyone else’s business. They’re my beliefs, not headlines.
Have you ever been “inconvenienced” by a political protest?
-Yes actually. Whether getting to my classes or just people stopping me and trying to cram their beliefs down my throat I have been inconvenienced many times. People will come up to me and yell at me they’re beliefs, and then criticize me on mine. I understand people are entitled to their beliefs and that’s all well and good, but let me get on with my day.
Do you think political protest should be criminalized?
-Honestly, if people are disturbing the peace and not allowing people to continue with their day, I do believe people should be arrested for disturbing the peace. People have a right to protest and get their point across, but the average joe has a right to be on time for their job or meeting. If you wanna protest, fine, but if you get so loud and so obnoxious that you create chaos, I hope you get booked.
I have never been in a political protest. I have been around them, while I would be walking in Washington DC but I did not know what they were protesting about. I have seen plenty of protest on tv like the Baltimore riot or the walkout that happened in my high school because they felt cheated out on not being able to vote for our president.
The only inconvenienced that I have had from a political protest was the traffic that arose from it. The reason for that is because they would walk on the roads to protest or block a road to get people to see their point.
I feel that politics should not be criminalized because they are just speaking their voice. However, when they start destroying something that when it should be a criminal act other then that is should not be criminalized.
Both the 1st amendment and 2nd amendment are really important to Americans. Freedom of speech is one of the things the United States is well known for. For me, people should be able to have possession of a gun if that’s what gets them through the night. However, they should at least have a background check before having a chance to be able to have possession of the gun.
I have never participated in a political protest nor have I ever been “inconvenienced” due to a political protest. But I know all of us have seen the news and seen many protest and of course many people inconvenienced because of it. The one I remember the most was when individuals would block major highways or roads, causes all traffic to cease. Thus creating a problem for commuters who need to go to work or people trying to reach the closest hospitable. I feel as though there are certain ways that groups can protest without causing problems for others. I do not believe that political protest should be criminalized. But I think once they start to become violent, there needs to be a stop to that activity. In regards to the 2nd amendment, I believe that it is a right of the people to bear arms, but also believe that there needs to be stricter rules in place on obtaining guns. Also local guns stores needs to have proper background checks, considering its way easier to purchase a gun at a private shop or even a gun show. Regarding the 1st amendment, everyone has their right to own opinions and they are perfectly fine with voicing those views. But once the situation escalates and starts to become a problem that is where I feel the event needs to stop.
I personally have never participated in a political protest before. I have seen many protests, mostly the ones that turn violent, on television. I have seen one political protest before in the town of Boyertown. Anyone who knows Boyertown knows that in the past there were a lot of KKK members who would hand out flyers on street corners and walk down the street like no big deal. Now, In 2017, the town has pushed out most of the members and is getting more diverse. I was once inconvenienced by a political protest when Black Lives Matter came to town where my father works. My father had to work the protest and I had to get a ride to Pittsburgh for my game with a teammate. The protest turned out very peacefully, not too many people ended showing up and the Police and the protesters actually talked and got along.
Political protests should not be criminalized, but at the same rate, protests should not turn violent, if one wants to protest something, one should be civilized and look like an organized group instead of resorting to violence and looking like animals. Throwing punches, damaging small businesses, or burning Police cars isn’t going to help you achieve what you want, but more or less, make the leaders of this country side against you.
I fully support the First and Second Amendment. Every American has the right of freedom of speech, religion, press, petition, and assembly. I think the First Amendment is the reason that The United States has grown into the country it is today and will continue to grow throughout the future as long as the citizens practice and keep their rights. I fully support the Second Amendment as well, citizens should have the right to bear arms (responsibly of course). The people of this country should not have rely solely on the government to protect them, there needs to be a back up plan, and that is what the Second Amendment is.
No, I have never participated in a political protest but I have friends and even past teachers that have participated in protests.
No, I have never been inconvenienced by a political protest. However, my mom has due to a political protest in Philadelphia where she goes to work.
Do you think political protest should be criminalized? I personally think that political protests should be criminalized. I understand why people support and participate in political protests but i personally do not think it is the way to go in terms of making efforts or getting a point across.
I believe and agree with the 2nd amendment and the right to bear arms. I believe that some modifications could be made, but it is a right that people should have. In terms of the 1st amendment, I think free speech is an important thing that we as Americans stand for but I think there should be certain measures or extremes that should limit how much is too much.
I have never participated in a political protest of any kind. I have never been inconvenienced by a political protest either. Also, I have never seen a political protest in person, but I have seen videos taken at protest and pictures. In some videos I have seen a lot of arguments between people who were against what people were protesting and I have also seen videos of police brutality at certain protests. I believe political protest should not be criminalized, because your first amendment is your right to freedom of speech, press, religion, petition the government, and the right to peacefully protest. A protest of any kind should not be criminalized just because of a handful of people who cannot protest peacefully and feel the need to express their worries with violence. I support both the first and second amendment because these are the rights that we a born with and cannot get taken away. Even though I support the first and second amendment I believe that there should be some regulations on both amendments. For the first amendment people who use or participate in any hate speech, hate crime against any religion, or any hurtful and violent protest that end up endangering the lives of others, should get arrested or pay a fine. For the second amendment gun control is a good thing. I believe that if you want and or need a gun for protection you should get a very detailed background check, have all your information on file (Needs to be up to date, if anything changes like address it needs to be changed in your file), fingerprints, and what type of gun and the number of bullets you buy should get recorded. If you have nothing to hide and your past is clean, then you should not have any problems with any gun control laws and regulations.
I have no participated in a political protest, but I have seen some on TV and through social media. I am from Rhode Island and there were many protests in downtown Providence that many of my friends attended so I saw them through their social media. I was not inconvenienced by them because I was never present during them, and just saw them through my friends.
Political protests should not be criminalized because everyone is allowed to believe in what they want. As long as there is not any violence during these protests I do not see why they should be criminalized. If they are used for a good purpose then they should be allowed.
I believe in and support the First and Second Amendments. Everyone should have the right to freedom of speech. I believe that people should have the right to bear arms, but there should be some rules and regulations that you have to pass in order to receive and carry a firearm. If a person does not seem suitable to carry a firearm, then they should not be granted one, but if you pass the rules and regulations then there should be no problem with carrying a firearm as long as you know how to use it.
I have not participated in a political protest, I have witnessed about two political protests though in person. I was younger so I didn’t quite remember much about what they were protesting about nor would I have understood it. All I remember was a group of people shouting with signs. I have seen many protests on TV, most of them have been about police brutality. I have never been inconvenienced by any political protests before.
I don’t think any protests should be criminalized. What is the point behind it? A peaceful protest should be enough to get a point across. A criminalized protest will cause more problems by separating the american citizens and government. We are supposed to be united as one nation.
Both the 1st and 2nd amendment are very important. Freedom of speech is an important right for every American to have. To add on to freedom of speech. If someone feels safer, while in possession of a gun then so be it. Some people need a gun to survive, while others feel safer with it.
I have never participated in any type of protest but I have been witness to some. I grew up in a small town in Pennsylvania and I recall many times as a child I viewed white supremacist groups on street corners, protesting. I was very young the first time I ever witnessed this, maybe 5 years old, and I didn’t understand what was happening but I remember it frightened me. Something about it scared me and felt wrong. That was a normal thing in my town when I was a child though. The street corner protests did slowly stop over the years, but to this day I am ashamed of it. It embarrasses me to know that kind of hate was freely expressed in my hometown.
Recently though, in the town I work in, a white supremacist group sent out a rather offensive drawing to every address in the town, which invoked a lot of fear in the people living there. Elderly people would come into my place of work and voice how much it scared them.
After witnessing this type of protest and hate throughout my life I completely agree that hate speech is not free speech.
I have never participated in a political protest but during my time living in Newark I have seen many! Protests can come about from many reasons but the protests I have seen have mainly been with workers demanding that their jobs treat them better. Poor working conditions, less then acceptable pay all could be the reason why people would protest outside of their jobs. Also I have seen protests at public parks about police brutality and as a community people should unite to try to prevent it. As many times I have seen a protest I have never been inconvenienced by one, they always seem to be held the opposite way that I was going.
Political protests should not be criminalized unless they become violent. Freedom of speech is the most important amendment and the amendment shouldn’t be upheld. As long as political protests stay non-violent and serve a beneficial purpose then they should stay legal.
I support both the 1st Amendment and the 2nd Amendment. Freedom of speech is an important aspect and being an American. Also the right to carry a fire arm is a necessity for some people. For the 2nd Amendment there are requirements you must meet to carry or gain access to a firearm legally. If the requirements are met and the person is fit to own a gun then they should be able too.
I have not participated in a political protest before but I have seen plenty on television and I almost saw one of them in person. I was never inconvenienced by a political protest because I ended up seeing it from afar, even if I don’t entirely remember what the cause was being protested for.
Political protests I believe shouldn’t be criminalized unless the severity of the protest causes more damage to people and the surrounding area than what it’s cause is worth for.
In terms of supporting absolutist interpretations of the second amendment of the constitution, I do believe that some people should be able to bear arms if need be, but only people who should be able to bear multiple weapons are those who have persistent checks to make sure that they are fit to hold a gun.